In the realm of energy storage, a seismic shift is underway. The phrase “Lithium is dead, long live the sodium” encapsulates this transformation, signaling a potential transition from lithium-ion to sodium-ion batteries. This evolution promises to redefine industries reliant on battery technology, from electric vehicles (EVs) to renewable energy storage. We are very excited for this change
Lithium is dead, The Rise of Sodium-Ion Batteries
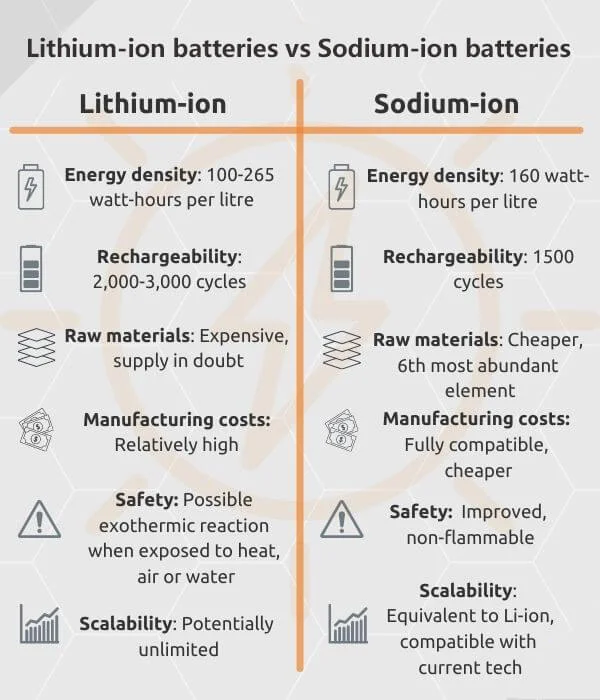
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are emerging as a formidable alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). While both technologies share similar operational principles—utilizing ion movement between electrodes to store and release energy—sodium offers distinct advantages.
Abundance and Cost-Effectiveness
Sodium is the sixth most abundant element on Earth, readily available in seawater and various minerals. In contrast, lithium is scarcer and geographically concentrated, leading to supply chain vulnerabilities and price volatility. The abundance of sodium translates to lower raw material costs for SIBs, making them an economically attractive option for large-scale energy storage applications.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
The extraction and processing of lithium often involve environmentally detrimental practices and raise ethical concerns, particularly regarding labor conditions in certain mining regions. Sodium extraction, by comparison, is less invasive and more environmentally friendly, offering a more sustainable pathway for battery production. Around the world there was enormous number of protests because of lithium mines, one of them was happened in Serbia
Safety and Performance
SIBs exhibit enhanced thermal stability, reducing the risk of overheating and combustion—a notable concern with LIBs. While SIBs currently have lower energy densities than their lithium counterparts, ongoing research aims to bridge this gap, with advancements in electrode materials and cell design showing promising results.
Industry Implications and Developments
The potential of SIBs is not merely theoretical; significant industry players are investing in this technology.
CATL’s Strategic Shift
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL), the world’s largest battery manufacturer, has launched a new sodium-ion battery brand, Naxtra. Robin Zeng, CATL’s CEO, has stated that sodium-ion batteries could potentially replace up to half of the market for lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, a segment CATL currently dominates. This strategic move underscores the company’s commitment to diversifying its battery portfolio and addressing the limitations of lithium-based technologies.
U.S. Initiatives
In the United States, Natron Energy is spearheading efforts to commercialize SIBs. The company has announced plans for a $1.4 billion sodium-ion battery factory in North Carolina, aiming to bolster domestic battery production and reduce reliance on foreign supply chains. Colin Wessells, Natron’s founder and co-CEO, emphasizes the importance of sodium-ion technology in achieving energy independence and sustainability goals.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the advantages, SIBs face challenges that must be addressed to achieve widespread adoption.
Energy Density
Currently, SIBs have lower energy densities compared to LIBs, making them less suitable for applications where space and weight are critical factors, such as in high-performance EVs. However, research into new electrode materials and cell architectures aims to enhance the energy density of SIBs, narrowing the performance gap.
Infrastructure and Scaling
The existing battery manufacturing infrastructure is heavily tailored to LIB production. Transitioning to SIBs will require significant investment in new manufacturing processes and supply chains. Nevertheless, the similarities in cell design between SIBs and LIBs could facilitate this transition, allowing manufacturers to adapt existing facilities with relative ease.
CATL founder and CEO Robin Zeng Yuqun has previously stated that sodium batteries could potentially replace up to half of the global LFP battery market.
“We will achieve mass production of the Naxtra battery by the end of this year. This will restructure the whole industry,” CATL marketing director Luo Jian said at a press conference in Shanghai last week.
Conclusion
The advent of sodium-ion batteries heralds a new era in energy storage, offering a more sustainable, cost-effective, and safer alternative to traditional lithium-based systems. While challenges remain, the concerted efforts of industry leaders and researchers signal a promising future for SIBs. As the world grapples with the dual imperatives of energy security and environmental stewardship, sodium-ion technology stands poised to play a pivotal role in powering the future.
